Department of Biology, University of Evansville
Biology Department, University of Detroit Mercy
Description
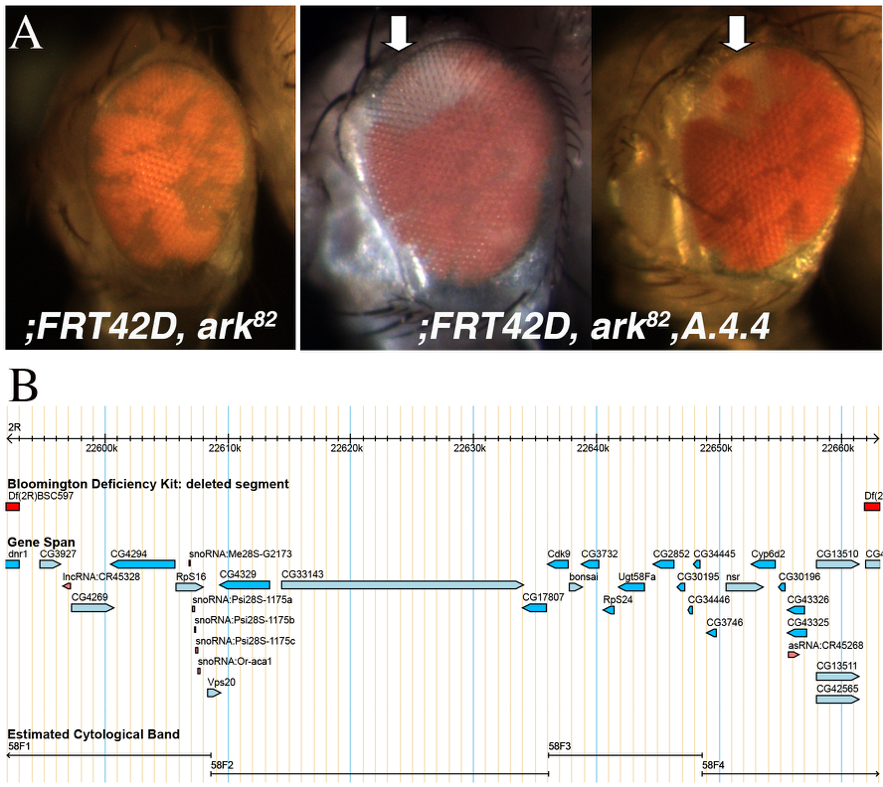
A novel Drosophila melanogaster mutant A.4.4 was isolated from a conditional Flp/FRT mosaic eye screen in the context of blocked apoptosis (Kagey et al., 2012). The ;FRT42D, Dark82 chromosome was used as a starting point for the EMS mutagenesis screen to screen to screen for mutations that conferred a growth advantage in the environment of blocked apoptosis via the homozygous Dark82 allele (Akdemir et al., 2006). Mutants were screened for over-representation of mutant tissue (pigmented) as compared to the Dark82 mosaic control (Figure 1A). The mutant mosaic phenotype generated by the cross FRT42D Dark82 A.4.4 X Ey>Flp; FRT42D resulted in mosaic eyes with a slight increase in the red:white ratio (approximately 70:30) as compared to FRT42D Dark82 control eyes (approximately 60:40). Ratios were estimated from observation of multiple mosaic eyes for each genotype. In addition to the increase in mutant tissue, the mosaic A.4.4 eye was observed with a consistent clone/patch of wild type (unpigmented) tissue at the dorsal peak of the eye (Figure 1A, arrow denotes observed region lacking mutant tissue). Whether this mutant phenotype is dependent upon this block in apoptosis is unknown at this time, however other mutant phenotypes in this screen have demonstrated a dependence upon a block in cell death (Kagey et al., 2012).
The genomic location of the homozygous lethal A.4.4 was mapped by deficiency mapping and complementation tests to identify the region on 2R that failed to complement. The location of the mutation was mapped by three independent groups of researchers that are part of the Fly-CURE consortium utilizing complementation mapping and the Bloomington Stock Center 2R Deficiency Kit (Cook et. al., 2012). We find that mutant A.4.4 failed to complement the deficiency Df(2R)X58-12/SM5. Mutant A.4.4 complemented the overlapping deficiencies Df(2R)BSC597/SM6a and Df(2R)BSC787/SM6a. Together these data create a failure to complement region of 2R:22,592,996..22,661,827 (Figure 1B). Additional complementation tests were set up with individual alleles of candidate genes found within this region and available at the BDSC and tested for lethality (Table 1). All of these crosses to individual alleles complemented A.4.4 suggesting that the mutation resides in one of the other genes within this genomic region. The initial complementation experiments were conducted in triplicate at three independent institutions, while the individual allele complementation tests were conducted once.
| Stock number
BDSC |
Gene affected | Genotype | Mating with A.4.4 |
| 12060 | Vps20 | P{PZ}Vps20rG270, l(2)rG270rG270/CyO | Complement |
| 16199 | CG4294 | y1 w1118; PBac{5HPw+}CG4294B316/CyO | Complement |
| 17065 | CG3927 | w[1118]; P{w[+mC]=EP}EP2515/CyO | Complement |
| 17739 | Ugt58Fa | w1118; PBac{PB}Ugt58Fac05973/CyO | Complement |
| 23049 | CG33143 | y1 w67c23; Mi{ET1}CG33143MB01293/CyO | Complement |
| 29511 | RpS24 | w*; P{FRT(whs)}G13 P{lacW}RpS24SH2053/CyO | Complement |
| 63874 | RpS16 | w1118; PBac{IT.GAL4}RpS160887-G4/CyO | Complement |
| 67706 | Vps20 | w*; Vps20I3/CyO | Complement |
Reagents
;FRT42D, ark82/CyO (Akdemir et al. 2006)
;FRT42D, ark82, A.4.4/CyO
Ey>Flp;FRT42D (BDSC 5616)
Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center 2R Deficiency Kit (Cook et al. 2012)
Individual alleles used for complementation tests (see Table 1 for BDSC numbers)
References
Funding
none
Reviewed By
Andrew ZelhofHistory
Received: September 10, 2018Accepted: December 15, 2018
Published: December 17, 2018
Copyright
© 2018 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Bieser, KL; Stamm, J; Aldo, AA; Bhaskara, S; Clairborne, M; Coronel Gómez, JN; Dean, R; Dowell, A; Dowell, E; Eissa, M; Fawaz, AA; Fouad-Meshriky, MM; Godoy, D; Gonzalez, K; Hachem, MK; Hammoud, MF; Huffman, A; Ingram, H; Jackman, AB; Karki, B; Khalil, N; Khalil, H; Ha, TK; Kharel, A; Kobylarz, I; Lomprey, H; Lonnberg, A; Mahbuba, S; Massarani, H; Minster, M; Molina, K; Molitor, L; Murray, T; Patel, PM; Pechulis, S; Raja, A; Rastegari, G; Reeves, S; Sabu, N; Salazar, R; Schulert, D; Senopole, MD; Sportiello, K; Torres, C; Villalobos, J; Wu, J; Zeigler, S; Kagey, JD (2018). The mapping of Drosophila melanogaster mutant A.4.4. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000069. Corrigendum in: microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000106.Download: RIS BibTeX