Description
The C. elegans ortholog of PIGN (phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class N) is encoded by pign-1. PIGN-1/PIGN is known to be an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphoethanolamine (EtNP) to the first mannose residue at precursors of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor (canonical function) and the enzymatic activity is essential for the viability of C. elegans (Gaynor et al., 1999; Hong et al., 1999; Ihara et al., 2017). We recently identified a non-canonical function of PIGN-1 to prevent protein aggregation within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) independently of its function in GPI biosynthesis (Ihara et al., 2017).
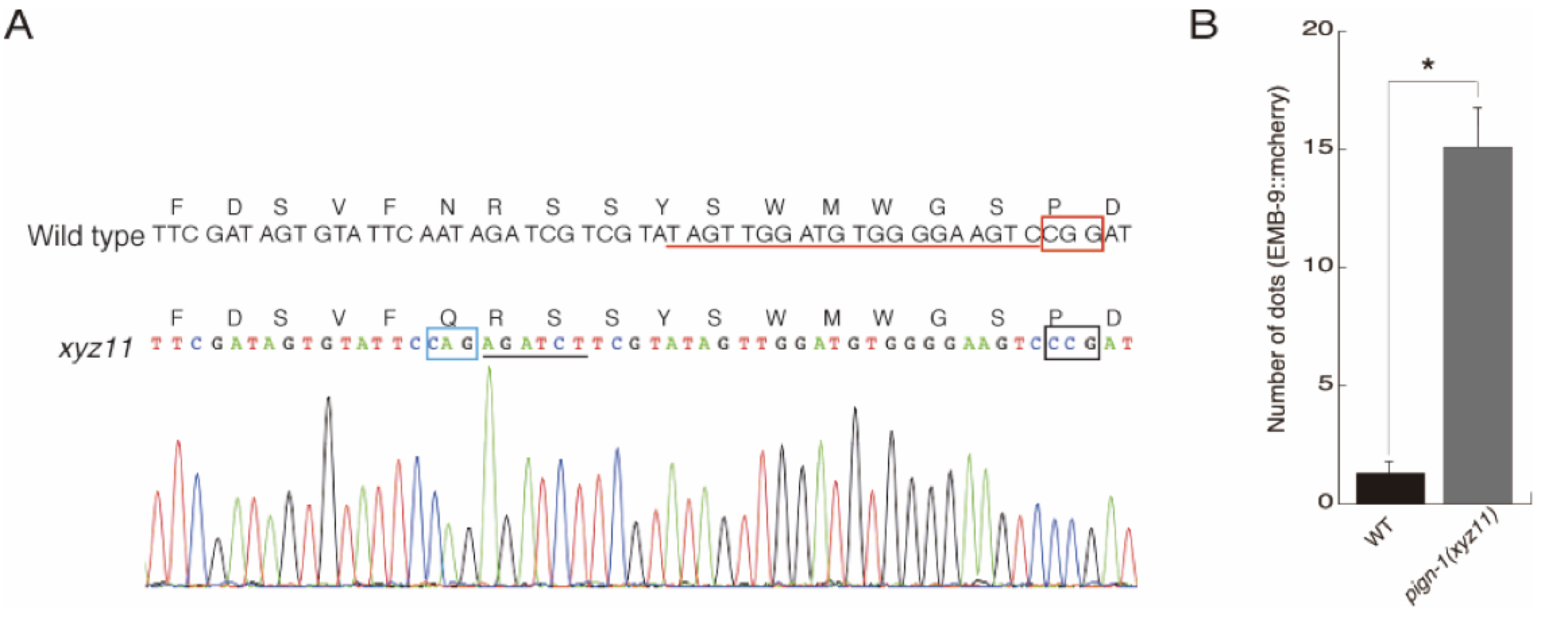
Although C. elegans pign-1 contains four potential N-glycosylation sites (N-X-S/T), the N127 (human N128) in the first loop at the ER side of PIGN-1 is only evolutionally conserved in yeast, worm, and vertebrate genomes (Gaynor et al., 1999). We examined GlycoProtDB which is a glycoprotein database providing information of Asn (N)-glycosylated proteins and confirmed really N-glycosylated at the asparagine 127 of PIGN-1 in C. elegans, GlycoProtDB (CELE_Y54E10BR.1) https://acgg.asia/db/gpdb/GPDB0000140. Using CRISPR/Cas9 genome engineering, we replaced asparagine 127 (human N128) in potential N-glycosylation site in the first loop at ER side of PIGN-1 with glutamine, which cannot be N-glycosylated (Figure 1A).
The pign-1(xyz11:N127Q) animal were measured for protein aggregation within the ER using EMB-9::mCherry (qyIs44), which is quantitatively measures the secretion efficiency from ER. Compared to wild-type animals, the pign-1(xyz11:N127Q) mutant showed a statistically significant protein aggregation in the body wall muscle cells (Figure 1B). In addition, pign-1(xyz11:N127Q) mutant was viable and fertile, suggesting that the EtNP transfer activity to GPI anchor was not disrupted.
Reagents
The qyIs44 [emb-9p::EMB-9::mCherry] was used for the injection strain. Animals were raised at 20 °C. The sgRNA vectors were microinjected together with 50 ng/ul single strand oligo, 50 ng/ul pDD162, and 50 ng/ul sur-5::gfp in qyIs44 animals. We selected candidate mutants based on abnormal localizations of EMB-9::mCherry, and confirmed the mutations using PCR.
The sgRNA plasmid was derived from Addgene plasmid 46169.
pDD162 (Peft-3::Cas9 + Empty sgRNA) vector from Bob Goldstein (Addgene plasmid # 47549 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:47549 ; RRID:Addgene_47549) was used for Cas9 expression (Dickson et al., 2013).
Single strand oligo used to generate xyz11: CCAGTTCAATTCGATAGTGTATTCCAGAGATCtTCGTATAGTTGGATGTGGGGAAGTCCCGATATTGTGAACCTTTTCGATGATCT. Strain: IHR-177 pign-1(xyz11)I. It will be sent to the CGC.
References
Funding
This work was supported by research grants from Presidential fund of National Institute of Technology, Ariake College and Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders.
Reviewed By
Kazuya NomuraHistory
Received: January 4, 2019Accepted: January 17, 2019
Published: January 18, 2019
Copyright
© 2019 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Narimatsu, T; Ihara, S (2019). New allele of C. elegans gene pign-1, named as xyz11. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000088.Download: RIS BibTeX