Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA
Current Address: School of Chemistry, University of the Republic, Montevideo, Uruguay
Description
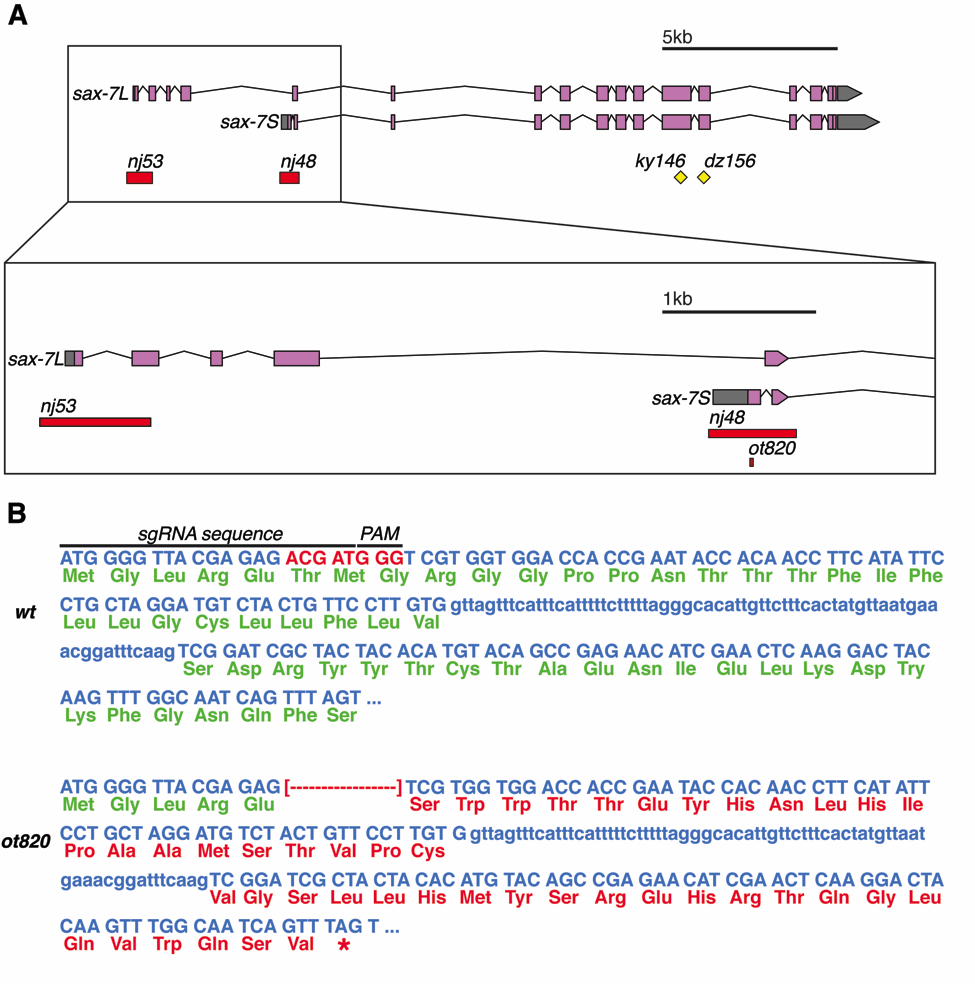
The immunoglobulin superfamily member sax-7 produces a long and short isoform that appear to have distinct functions (Chen et al. 2001; Wang et al. 2005; Sasakura et al. 2005; Pocock et al. 2008). An isoform-specific allele for the long isoform, sax-7L, was previously reported (Sasakura et al. 2005), but an isoform-specific allele for the short isoform, sax-7S, has been lacking (Fig. 1A). We used CRISPR/Cas9 to generate such an allele, using the unc-22 co-CRISPR method (Kim et al. 2014). The ot820 allele was isolated using sgRNA targeted to the first exon of sax-7S (sgRNA sequece: 5’ – TGGGGTTACGAGAGACGAT – 3’). Twitching progeny were screened by PCR and Sanger sequencing, and an 8bp deletion 15bp from the start codon was isolated (screening primers: 5’ – GGTGCTTCTCTGGTGGTAGC – 3’ and 5’ – TGTTGGCAAACAAAATACACG – 3’, Fig. 1B). While the sax-7L isoform is predicted to be entirely unaffected by this allele, the resultant frameshift is predicted to generate a 49 amino acid protein in which all but the first five amino acids of sax-7S are aberrant and has no predicted signal sequence, before terminating in a premature stop in the second exon (Fig. 1B). This allele therefore likely represents a null for the sax-7S isoform. After we generated this allele, a recent paper reported an additional sax-7S-specific allele, with somewhat similar, but not identical sequence properties (Chen et al., 2019). Consistent with previous evidence of distinct functions of sax-7 isoforms, these authors showed differing axon fasciculation defects between these two alleles, which is further distinct from a total null allele. These new sax-7S alleles should help to reveal new insights into the role of L1CAM/SAX-7 isoforms in the nervous system.
Reagents
OH13830 sax-7(ot820) IV; oyIs14 V. Will be available at CGC.
References
Funding
This work was supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Reviewed By
AnonymousHistory
Received: March 4, 2019Accepted: March 22, 2019
Published: March 27, 2019
Copyright
© 2019 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Rahe, D; Carrera, I; Cosmanescu, F; Hobert, O (2019). An isoform-specific allele of the sax-7 locus. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000092.Download: RIS BibTeX