Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100101, China
Neurobiology Section, Division of Biological Sciences, University of California, San Diego, CA92093
Description
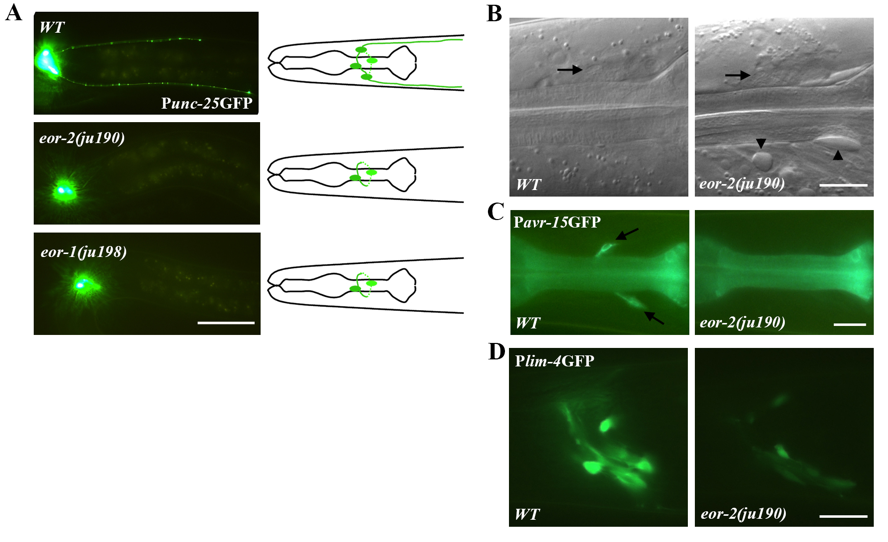
In a visual screen for genes that regulate the pattern of the juIs76[Punc-25GFP] marker, which labels four GABAergic RME neurons and 19 ventral cord D-type neurons (Huang et al., 2002), we isolated two mutants, eor-2(ju190) and eor-1(ju198) (Huang and Jin, 2019). In both eor-2(ju190) and eor-1(ju198) mutants, Punc-25GFP expression was almost completely abolished in RMED/V cells, whereas RMEL/R cells and the D neurons showed normal morphology (Figure 1A). We observed similar defects with a different Punc-25GFP transgene. The absence of Punc-25GFP expression was seen in all larval stages and adults, was more frequent in RMED than in RMEV cells. For example, 98% of eor-1(ju198) animals lost Punc-25GFP expression in RMED and 67% in RMEV (N=100). ju198 behaves as a partial loss of function mutation because 100% and 94% of eor-1(cs28) animals do not express Punc-25GFP expression in RMED and RMEV, respectively (N=100) (Huang and Jin, 2019). eor-2(ju190)animals also displayed mild Unc, low penetrant Egl and rod-like lethality. The loss of Punc-25GFP expression in eor-2(ju190) and eor-1(ju198) could be due to cell fate alterations or cell death. To distinguish between these possibilities, we first examined the cell body positions of RMED and RMEV cells under Nomarski microscope (Huang et al., 2004). In both eor-2(ju190) and eor-1(ju198) mutants, the RMED and RMEV cells were found in their normal locations (Figure 1B). We also made double mutants of eor-2(ju190) and ced-3(n717), which blocks apoptosis, and found that eor-2(ju190); ced-3(n717) double mutants showed absence of Punc-25GFP expression in RMED/V, similar to eor-2(ju190) single mutants, indicating that ineor-2(ju190) and eor-1(ju198) animals, the RMED and RMEV cells are alive, but that their differentiated traits are likely altered.
To further examine whether other properties of the RMED/V cells might be altered in these mutants, we looked at the expression of Pavr-15GFP, which is normally expressed in both RMED and RMEV neurons (Dent et al., 1997) and Plim-4GFP transgenes, which is normally expressed in RMEV neuron and some other head neurons (Sagasti et al., 1999). We found that in eor-2(ju190) animals,Pavr-15GFP was not expressed in RMED/V (Figure 1C), the GFP intensity from Plim-4GFP transgene was greatly reduced, but not abolished, in all expressing cells (Figure 1D). These data show that eor-2(ju190) alters multiple differentiated aspects of RMED/V neurons.
Acknowledgments
We thank C.Bargmann for Plim-4GFP, L. Avery for Pavr-15GFP reporters. We appreciate valuable discussions with O. Hobert for communicating unpublished results.
References
Funding
NIH R01 NS 035546
Reviewed By
Oliver HobertHistory
Received: July 1, 2019Accepted: July 18, 2019
Published: July 31, 2019
Copyright
© 2019 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Huang, X; Jin, Y (2019). EOR-1 and EOR-2 function in RMED/V neuron specification. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000138.Download: RIS BibTeX