Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100101, China
Neurobiology Section, Division of Biological Sciences, University of California, San Diego, CA92093
Description
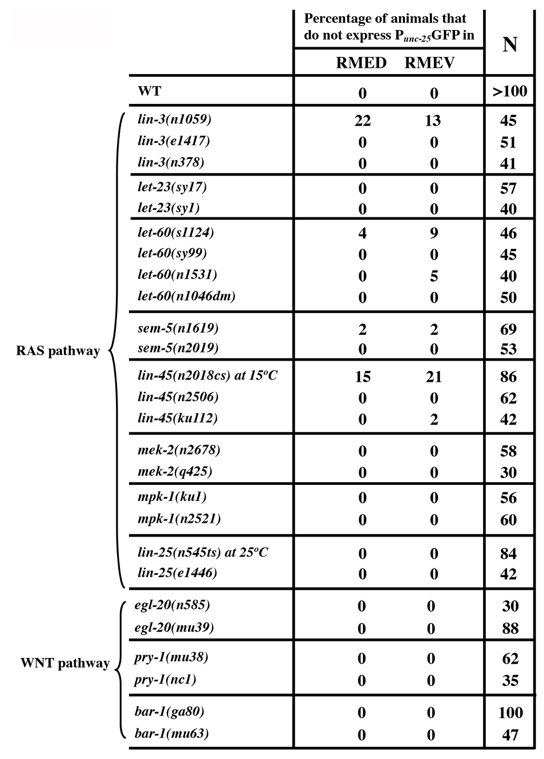
We found that loss of either eor-1 or eor-2 function results in identical differentiation defects in RMED/V neurons (Huang and Jin, 2019a; Huang and Jin, 2019b). EOR-1 and EOR-2 are thought to positively regulate RAS and WNT signaling pathways in vulval cell induction and in P12 cell fate specification (Howard and Sundaram, 2002). Genetic double mutant analysis suggests that eor-1 and eor-2 function redundantly with the Mediator complex proteins sur-2 and lin-25 (Howard and Sundaram, 2002). We wished to test whether RAS and WNT signaling pathways are involved in RMED/V differentiation. We examined Punc-25GFP expression in several RAS and WNT mutants (Huang et al., 2004). In the canonical RAS signaling pathway, the EGF-like growth factor LIN-3 binds its receptor LET-23, which then activates LET-60/ras and the MAP kinase cascade that includes LIN-45/raf (MAPKKK),MEK-2/MEK (MAPKK) and MPK-1/ERK (MAPK). We examined strong loss-of-function or putative null mutations in these genes. We detected mild defects in RMED/V cells in lin-3(n1059) and lin-45(n2018cs) mutant animals. Twenty-two percentage of lin-3(n1059) mutants lost Punc-25GFP expression in RMED, and 13% lost the expression in RMEV (N=45). Fifteen percentage and 21% of lin-45(n2018cs) animals at non-permissive temperature did not express Punc-25GFP in RMED and RMEV, respectively (N=86) (Table 1). However, similar phenotypes were not found in several other alleles of lin-3 and lin-45 (Table 1). In addition, mutations in LET-23/EGFR, SEM-5, an adaptor protein, MEK-2/MAPKK and MPK-1/MAPK, had little or no effects on Punc-25GFP expression in RMED/V (Table 1). The let-60(n1046) dominant mutation also did not affect RMEs. lin-25 has been shown to act in parallel to eor-1 and eor-2 in vulva induction, and also did not show any effects on RME. We observed similar results in mutants for the canonical WNT signaling genes including egl-20/WNT, pry-1/Axin and bar-1/b-catenin (Table 1). Therefore, these data suggest that the function of EOR-1 and EOR-2 in RMED/V neurons is likely independent of canonical RAS and WNT pathways.
Reagents
The mutations used are listed below: Linkage group LGI: mek-2(n2678), mek-2(q425); LGII: let-23(sy17), let-23(sy1); LGIII: mpk-1(n2521), mpk-1(ku1); LGIV: lin-3(n1059), lin-3(e1417), lin-3(n378), eor-1(cs28), eor-1(ju198), lin-45(n2018), lin-45(n2506), lin-45(ku112), let-60(s1124), let-60(sy99), let-60(n1531), let-60(n1046), egl-20(n585), egl-20(mu39); LGV: lin-25(n545), lin-25(e1446), pry-1(mu38), pry-1(nc1), daf-21(nr2081), daf-21(p673); LGX: sem-5(n1619), sem-5(n2019), eor-2(cs42), eor-2(ju190), bar-1(ga80), bar-1(mu63).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate valuable discussions with O. Hobert for communicating unpublished results.Some of the strains used here were obtained from the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center,which is supported by the NIH.
References
Funding
NIH R01 NS 035546
Reviewed By
Oliver HobertHistory
Received: July 1, 2019Accepted: July 18, 2019
Published: July 31, 2019
Copyright
© 2019 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Huang, X; Jin, Y (2019). EOR-1 and EOR-2 act independently of RAS and WNT signaling pathways in RMED/V neuron specification. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000140.Download: RIS BibTeX