Description
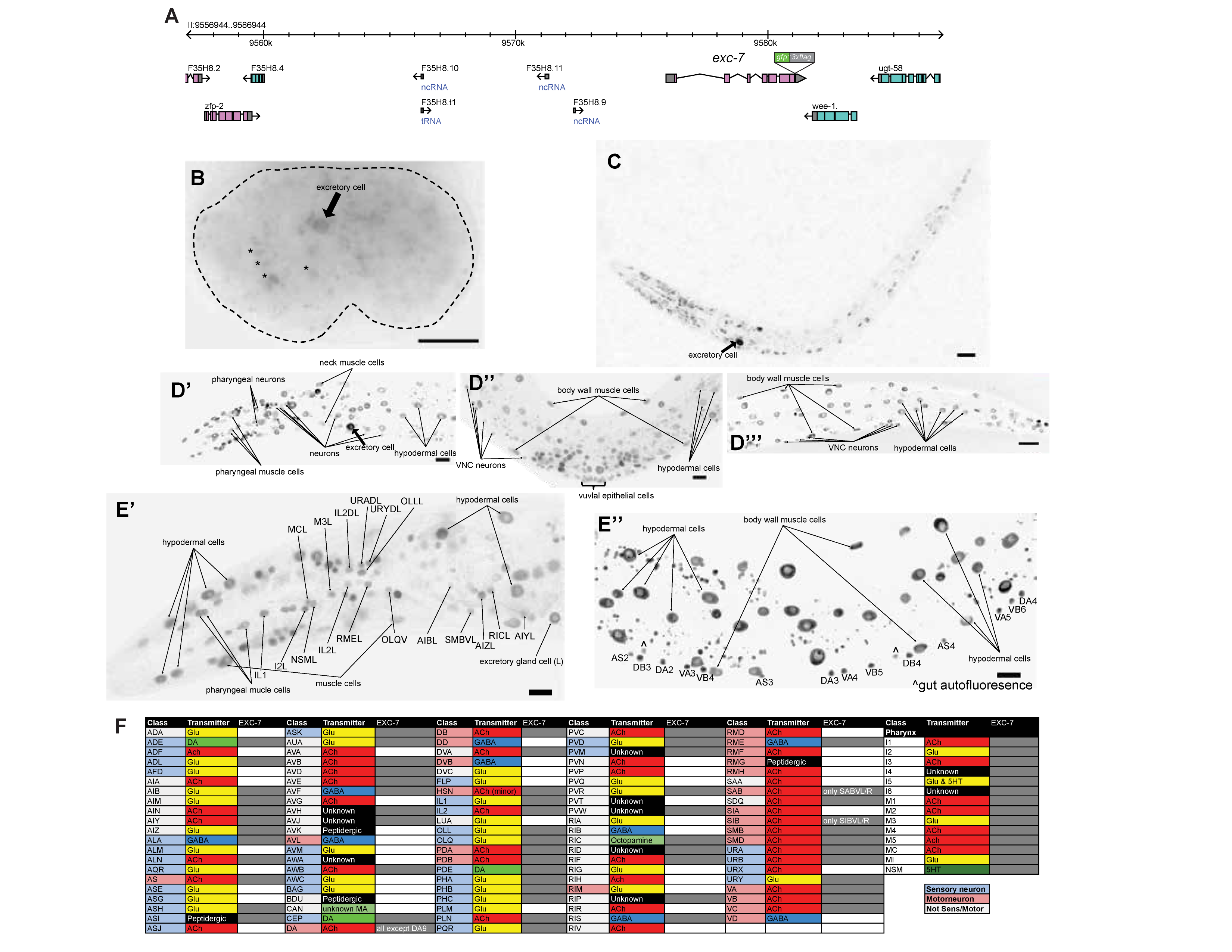
We are interested in identifying genes that are expressed in a panneuronal manner throughout the nervous system (Stefanakis et al., 2015). The Drosophila elav locus is a panneuronally expressed RNA binding protein (Campos et al., 1987; Robinow and White, 1988). Elav protein staining is routinely used in Drosophila to identify neurons and cis-regulatory control regions from the elav locus are routinely used as panneuronal Gal4 drivers (Berger et al., 2007; Luo et al., 1994; O’Neill et al., 1994; Osterwalder et al., 2001; Robinow and White, 1991). Based on sequence homology, the C. elegans exc-7 locus is the sole C. elegans orthologue of elav (Fujita et al., 2003; Fujita et al., 1999; Loria et al., 2003; Samson, 2008). Previous expression pattern analyses have shown that exc-7 is expressed only in a subset of neurons of the nervous system (the expressing neurons were mostly unidentified) (Fujita et al., 1999; Loria et al., 2003). However, reporter gene constructs previously used to infer exc-7 expression did not contain all intergenic region of the large exc-7 locus. Therefore, the possibility remained that through the use of more distal cis-regulatory elements, C. elegans exc-7 could also be panneuronally expressed, like its fly orthologue. To address this possibility, we tagged endogenous exc-7 with gfp::3xflag at its C-terminus using CRISPR/Cas9 genome engineering (Dokshin et al., 2018) and examined its expression. We cloned gfp from the che-1(ot856[che-1::gfp]) allele (Leyva-Diaz and Hobert, 2019), inserted it into the pMiniT 2.0 vector (NEB), and used that resulting plasmid for subsequent cloning of the gfp tag.
Embryonic expression of exc-7 was first observed at the bean stage. By reverse lineaging with use of SIMI-Biocell software (Schnabel et al., 1997), we confirm the identity of one of the expressing cells at this stage as the excretory canal cell (Fig. 1B, arrow). In L1 animals, broad expression in the head, ventral nerve cord (VNC), and tail was observed (Fig. 1C). In young adults, expression is notably observed in vulva cells (Fig. 1D’’). In the nervous system specifically, expression is observed in many neurons throughout the body (Fig. 1D’-D’’’), but unlike Drosophila Elav, exc-7::gfp it is not panneuronally expressed. We used the NeuroPAL transgene (https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/676312v1) to individually identify each neuron in which exc-7 is expressed in the young adult worm. Sites of expression are listed in Fig. 1F and some examples of neuronal expression are shown in Fig. 1E’. Expression in all neurons is at least several fold more intense than UPN::NLS::TagRFP-T signal from NeuroPAL. We confirmed previously reported expression in cholinergic VNC MNs, but absence of GABAergic VNC MNs (Fig. 1E’’), consistent with previous reports (Fujita et al., 1999; Loria et al., 2003) and consistent with exc-7 functioning in cholinergic, but not GABAergic neurons to control alternative splicing (Norris et al., 2014). exc-7::gfp is also expressed in some non-neuronal cell types, including muscle and hypodermis, but not in the gut (Fig. 1D’-D’’’). A previous report showed that exc-7 is only transiently and weakly expressed in the excretory cell, which, based on exc-7’s excretory mutant phenotype, has puzzled researchers (Fujita et al., 2003). We find that the gfp tagged exc-7 locus is strongly and continuously expressed in the excretory canal cell (Fig. 1B-D’, arrow). We conclude that unlike its fly orthologue elav, exc-7 is not a panneuronally expressed gene.
Reagents
OH16020: exc-7(ot970[exc-7::gfp::3xflag])
The strain is available through the CGC.
Acknowledgments
We thank Chi Chen for expert DNA injection, Eduardo Leyva-Díaz for advice with CRISPR genome editing, and Neda Masoudi for help with embryonic lineaging.
References
Funding
This work was supported by the HHMI.
Reviewed By
Matthew BuechnerHistory
Received: October 19, 2019Accepted: October 30, 2019
Published: October 30, 2019
Copyright
© 2019 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Pham, K; Hobert, O (2019). Unlike Drosophila elav, the C. elegans elav orthologue exc-7 is not panneuronally expressed. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000189.Download: RIS BibTeX