Description
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression during animal development. Large scale efforts to identify functions of individual miRNAs or miRNA families provide invaluable insight into the roles these miRNAs play in organism development (Miska et al. 2007, Alvarez-Saavedra and Horvitz 2010), however, some miRNA genes lack deletion alleles. To our knowledge, no alleles in C. elegans mir-1022 gene are currently available.
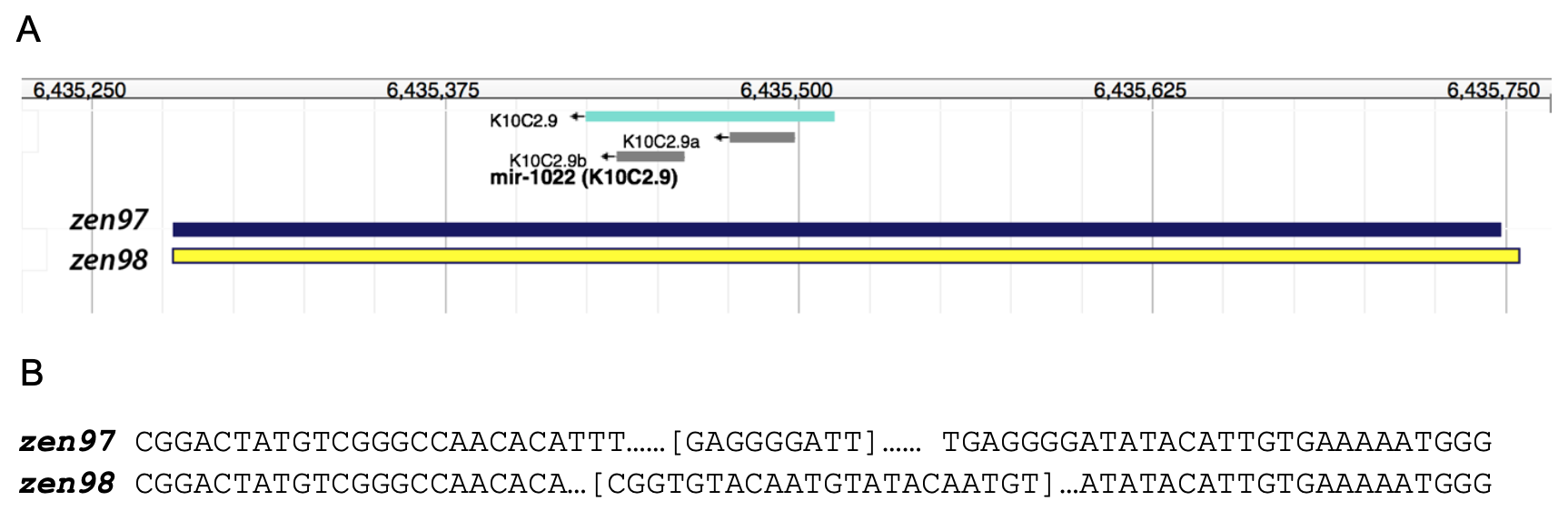
Using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing technique, we generated two novel alleles in the mir-1022 locus in C. elegans (Fig 1A). The zen97 allele is a 498 pair deletion of the mir-1022 locus which also inserts GAGGGGATT into that locus (Fig 1B). The zen98 allele is a 508 base pair deletion from the mir-1022 locus, inserting CGGTGTACAATGTATACAATGT in that location (Fig 1B).
To specifically target the mir-1022 locus for editing, we used the following guide RNAs: mir-1022_gRNA 1: 5’-TCGGGCCAACACATTTCAG-3′ and mir-1022_gRNA 2: 5’-TTTGCGTGCGAAAGTGGTGA-3′. The primers used for PCR genotyping were mir-1022.for3: 5’-CTAGTGCATTGTCCAGGCAG-3′ and mir-1022.rev3: 5’-CGTGATCTCTTGGTGCACAT-3’. The Co-CRISPR marker dpy-10 was used in order to more easily identify worms with active CRISPR/Cas9 as previously described (Arribere et al. 2014). CRISPR components were injected into N2 animals as an RNP complex (Paix et al. 2015). Alt-R Cas9 (cat# 1081058), mir-1022 and dpy-10 Alt-R® CRISPR-Cas9 crRNAs (custom), and tracer RNA (cat# 1072532) were purchased from IDT. PCR screening identified two independent mutations, each disrupting the mir-1022 locus (Fig 1), which were subsequently homozygosed and sequenced. UY262 mir-1022(zen97) did not segregate any dumpy, dumpy roller, or roller animals and was not outcrossed. mir-1022(zen98) was outcrossed once to wild type (N2) males to remove a background dpy-10 mutation, generating the 1x outcrossed UY286 mir-1022(zen98) strain. Sequencing was repeated to confirm the mutation.
Both alleles are homozygous viable. While not extensively characterized, no gross morphological phenotype was produced by either mir-1022 allele. Further phenotypic analysis will be necessary to determine the exact effect of the two mir-1022 mutations.
Reagents
UY262 mir-1022(zen97) and UY286 mir-1022(zen98) (1x outcrossed) are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
These deletions were created during the course of BIOL676 Molecular Genetics at Kansas State University. We thank the Fall 2019 BIOL676 section students for their assistance with screening.
References
Funding
Funding for BIOL676 is provided by Kansas State University. This work was in part supported by R35GM124828 to A.Z.
Reviewed By
Katherine McJunkinHistory
Received: February 5, 2020Accepted: March 27, 2020
Published: April 1, 2020
Copyright
© 2020 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Horn, C; Sholl, R; Haskell, D; Hebbar, S; Zinovyeva, A (2020). Two new CRISPR-generated alleles in the C. elegans mir-1022 gene.. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000233.Download: RIS BibTeX