Description
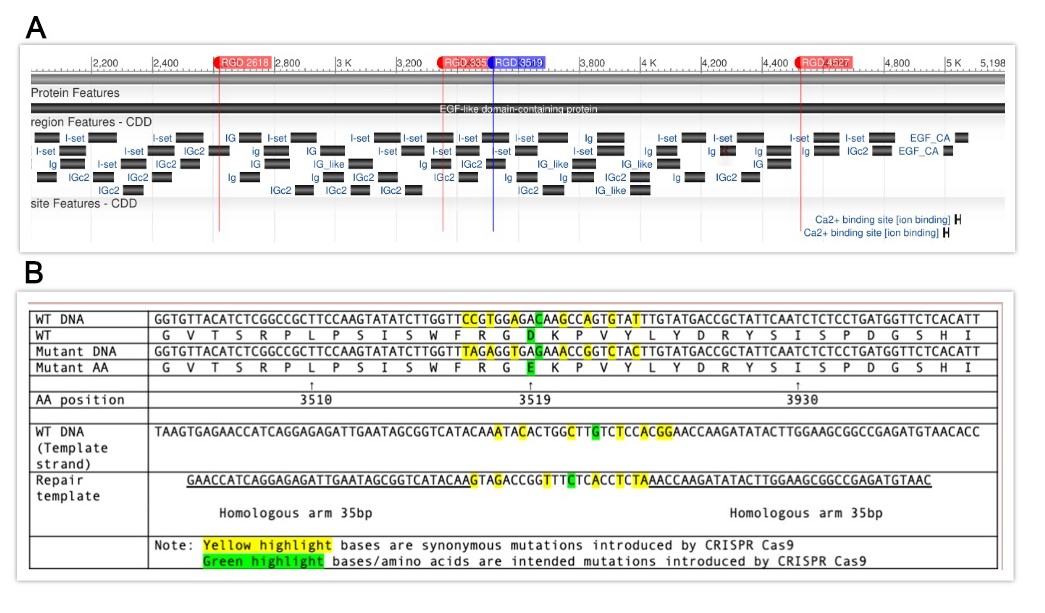
The him-4 gene in Caenorhabditis elegans is involved in important developmental processes in the organism including basement membrane attachment, anchor cell invasion, defective cytokinesis, and gonad positioning along the basement membrane (Morrissey et al., 2014). The human ortholog to him-4, HMCN 1 (hemicentin-1), is implicated in age related macular degeneration 1 (Thompson et al., 2007). HIM-4/HMCN1 is a highly conserved extracellular matrix structural component and contains six RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) cell-binding motifs within its 48 immunoglobin (Ig)-like repeats, while HMCN1 contains only one RGD motif (Vogel and Hedgecock, 2001). Two novel mutant alleles of C. elegans him-4 were generated using CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing in this study. In one mutant allele, three of the aforementioned six RGD motifs were mutated to RGE (Arg-Gly-Glu) (Takahashi et al., 2007). Four of the six RGD motifs were altered to RGE in the second mutant line. Neither of these mutant lines exhibited outstanding abnormal phenotypes when screened for behavioral or morphological abnormalities. We examined the mutants for Him (high incidence in male) phenotype, kq8207 (0% male, n=888) and kq8297 (0.1% male, n=963). However, the examined animals failed to show an outstanding number of males compared to N2 (0%, n=582). Mutants were also examined for behavioral abnormalities in a thrashing assay. A Mann-Whitney U Test revealed possible differences between kq8207 mutants and N2 worms (p=0.037), and revealed no significant difference between kq8297 mutants and N2 worms (p=0.447). 53 triple RGD mutants (average 19.85 thrashes), 51 RGD quadruple mutants (average 21 thrashes), and 51 N2 worms (average 22.16 thrashes) were used in this assay. Morrissey et al. demonstrated that PAT-3/INA-1integrin is essential for assembly of HIM-4/hemicentin puncta during anchor cell invasion (Morrissey et al., 2014). However, integrin and HIM-4 failed to colocalize in other tissues (Vogel and Hedgecock 2001; Morrissey et al., 2014). Although anchor cell invasion was not examined in this study, these him-4 RGD mutants hold potential for further research pertaining to the functions of cell to extracellular matrix binding domains in C. elegans.
Methods
Request a detailed protocolIn order to induce specific RGD to RGE mutations in him-4, CRISPR target sites were identified within the gene using the CRISPR guide RNA Selection Tool (http://genome.sfu.ca/crispr/). The triple mutation line, BU8207 (him-4(kq8207)), contains RGE mutations at amino acid numbers 2618, 3352, and 4527 (Figure A), in which the mutations were added sequentially into each position. The quadruple mutation line, BU8297 (him-4(kq8297)), contained these three loci as well as amino acid number 3519 as described here. Briefly, the mixture of custom template DNA (Temp-4HIM4RGE3519, Figure B), custom crRNA (HIM4RGD3519), tracrRNA (cat. #1072532), and Alt-R Cas9 nuclease (cat. #1081058) was annealed at room temperature (Paix et al., 2015) and micro-injected into the syncytial gonad arms of N2 wild-type worms (P0) (Mello et al., 1991). The mixture also included dpy-10 crRNA as a co-CRISPR marker (Arribere et al., 2014). The F1 generation was then screened for the intended mutation by identifying animals exhibiting the Dpy phenotype and by PCR genotyping using mutation specific primers (HIM4RGE3519R and HIM4RGE3519SEQF). PCR was then conducted on F2 offspring using both wild-type him-4 and mutant-specific primers (HIM4RGD3519WTR and HIM4RGE3519SEQF) in order to isolate homozygous mutants. Once homozygotes were isolated, PCR products were sequenced in order to confirm that the mutation was successful (Psomagen Inc, Rockville, MD). The repair DNA (as well as all other oligos used to create these mutant lines) for these loci was designed and produced at IDT Inc., Coralville, IA. Both lines of mutant animals were backcrossed (1x) to N2 then studied for phenotype characterization. For Him phenotypes, N2, kq8207, and kq8297 worms were self-fertilized, and males were randomly identified from NGM agar plates. The thrashing assay was performed by counting the number of body bends for 15 seconds in a 10 μl drop of M9 buffer (Lee et al., 2005). A Mann-Whitney U Test was then run to confirm statistical significance of results.
crRNA sequence
HIM4RGD3519 AAUACACUGGCUUGTCUCCA
(dpy-10) ZQDP10A GCUACCAUAGGCACCACGAG
PCR Primers
HIM4RGE3519SEQF TACGCCGCAGAAGTGATTGG
HIM4RGE3519SEQR TCCTGCTTCGTTGGATGCAC
HIM4RGD3519WTR ATACACTGGCTTGTCTCCACGG
HIM4RGE3519R ACAAGTAGACCGGTTTCTCACCTCTA
Repair oligo, crRNA, and primer sequences for screening are readily available upon request.
Reagents
BU8207 him-4(kq8207) and BU8297 him-4(kq8297) are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
These mutant lines were created during the course of BIO 4108 Cell and Developmental Biology Lab at Baylor University. We would also like to thank Angela Leung for her assistance in this study.
References
Funding
Funding for BIO 4108 is provided by Baylor University.
Reviewed By
AnonymousHistory
Received: April 23, 2020Revision received: May 9, 2020
Accepted: May 9, 2020
Published: May 10, 2020
Copyright
© 2020 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Park, A; Qiu, Z; Lee, M; Lewis, K; Cross, M; Baur, O; Brice, S; Whiteley, L (2020). Triple and quadruple mutation of RGD motif using CRISPR-Cas9 in him-4 locus of Caenorhabditis elegans. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000249.Download: RIS BibTeX