Description
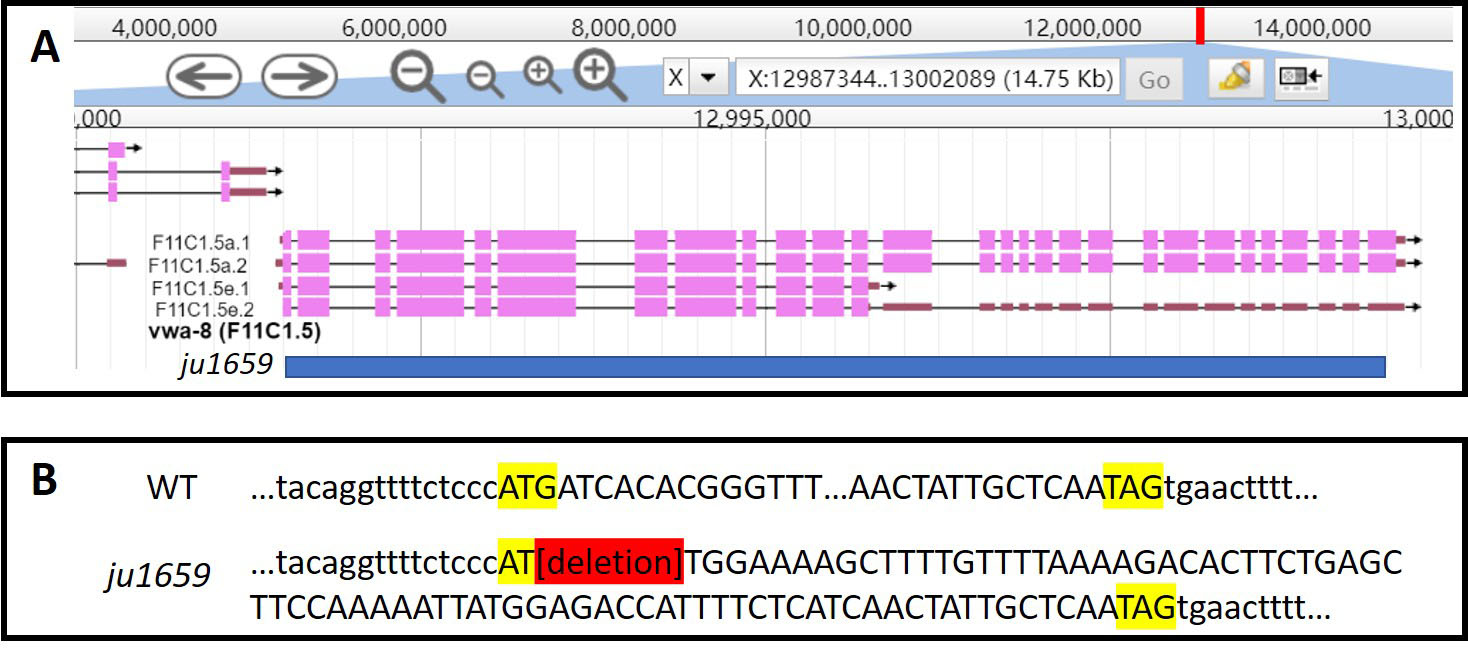
VWA8 proteins, named for von Willebrand factor A (VWA) domain containing 8, are conserved from worm to mammals (Whittaker & Hynes, 2002). In human, two SNPs (rs9566845 and rs9566867) in vwa8 are found to be associated with bipolar disorder with comorbid migraine (Oedegaard et al., 2010). Another SNP (rs9532931) is tentatively associated with a specific sub-group of autism patients (Anney et al., 2010). The C. elegans VWA-8 long isoform shares 38% and 55% amino acid sequence identity and similarity, respectively, with human VWA8 long isoform. We showed that endogenous VWA-8 is expressed in mitochondria of somatic tissues, except neurons (Zhu, Chisholm & Jin, 2020). To determine the function of C. elegans vwa-8, we generated a null allele vwa-8(ju1659) by CRISPR-Cas9. vwa-8(ju1659) mutants are homozygous viable, and indistinguishable from wild type in gross phenotypes such as body size, brood size, growth rate and movement.
Methods
Request a detailed protocolWe generated vwa-8(ju1659) using two CRISPR RNA (crRNAs), 5’-AGTGAAACCCGTGTGATCAT-3’ and 5’-CTACAACGAGAGTTGCCTGT-3’ (Integrated DNA Technologies) targeting the start and stop codons of vwa-8, respectively. The crRNAs were injected into wild type hermaphrodites with purified Cas9 protein (MacroLabs, University of California Berkeley), trans-activating crRNA (tracrRNA) and dpy-10 crRNA, as described (Paix, Folkmann, Rasoloson, & Seydoux, 2015). The dumpy F1 progeny of the injected P0 wild type animals were singled to separate plates. F1 dumpy worms were then genotyped for the presence of potential vwa-8 deletions using the following primers: 5’-CCTCGAGGGCCCCATATTTT-3’ and 5’-TGCTCTCGAACACCTTGCTT-3’. Several independent vwa-8 deletions were identified. All deletion mutants behaved similarly. ju1659 is a 7989bp deletion of vwa-8 which removes nearly all the coding sequence of vwa-8, except the last 82bp of the last exon. CZ26606 vwa-8(ju1659) was generated after outcrossing with N2 for 3 times to remove the dumpy mutation.
Reagents
CZ26606 vwa-8(ju1659) will be available at the CGC.
Acknowledgments
We thank members of the Jin and Chisholm laboratories for valuable discussions. We acknowledge WormBase as an information resource.
References
Funding
This work was supported by NIH R01 NS093588 to AC and YJ and R01 GM054657 to AC.
Reviewed By
AnonymousHistory
Received: May 20, 2020Revision received: June 1, 2020
Accepted: June 2, 2020
Published: June 7, 2020
Copyright
© 2020 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Zhu, M; Chisholm, AD; Jin, Y (2020). A null mutation of C. elegans vwa-8. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000263.Download: RIS BibTeX