California State University Stanislaus, Turlock, CA 95382
Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO 63130
Description
Introduction
The Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb) encodes a Ras homolog (Karassek et al. 2010). Ras is family of genes that make proteins involved in cell signaling pathways that control cell growth and cell death (Banerjee and Resat 2016). The gene model reported here (dgri_Rheb) was developed for the May 2011 assembly of D. grimshawi Agencourt dgri_caf1/DgriCAF1 (GCA_000005155.1) to describe the ortholog to D. melanogaster Rheb(FBgn0041191) at the locus previously annotated as XM_001989756.1. The general protocol and datasets for the genome browser tracks used to establish this reported gene model are reported in Rele et al. 2020. Additional tools and resources used in generating and confirming this model include HISAT (Kim et al. 2015), BEDTools (Quinlan et al. 2010), and the Sequence Read Archive (trace.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Traces/sra/?study=SRP073087).
Synteny
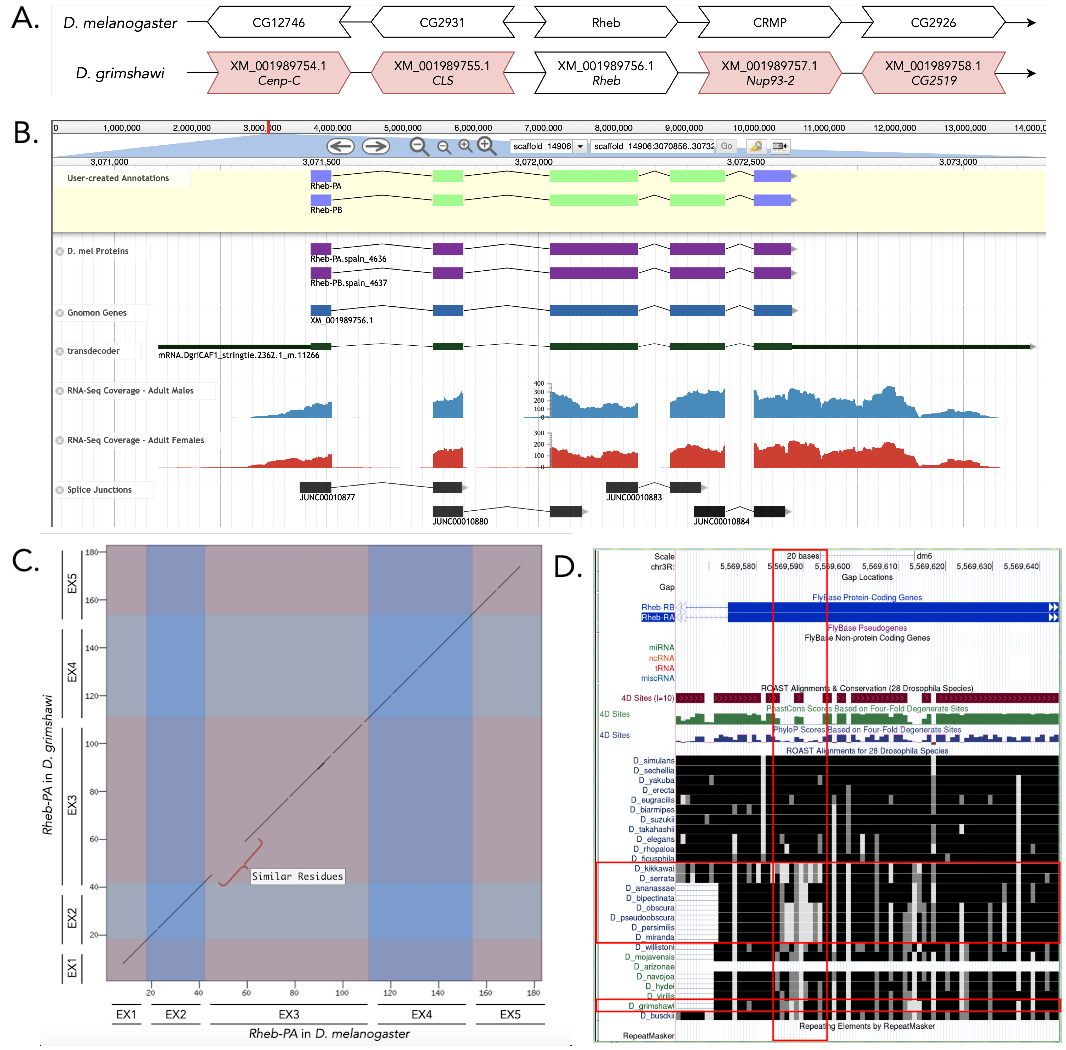
The Rheb gene on chromosome 3R in D. melanogaster is surrounded by the genes CG12746, CG2931, CRMP, and CG2926. Upon a tblastn search, the Rheb ortholog gene in D. grimshawi, on scaffold 14906, is surrounded by the genes XM_001989754.1, XM_001989755.1, XM_001989575.1, and XM_001989576.1 (orthologous to Cenp-C , CLS, Nup93-2, and CG2519) in D. melanogaster, Figure 1A). Though none of these flanking genes appear to be orthologous between the two species, we determined this region to contain the ortholog for Rheb in D. grimshawi because this location had a substantially better blastp hit to the Rheb protein sequence than to the second-best hit.
Gene Model
This gene model contains two isoforms of the Rheb protein in D. grimshawi, Rheb-PA and Rheb-PB (Figure 1B). Each of these isoforms contains five identical coding exons. The model in D. melanogaster and D. grimshawi have the same length and number of exons, and are similar in peptide sequence. However, there is a dissimilarity at the start of the third exon; but the peptides replacing the ones in D. melanogaster have similar properties. The coordinates of the corrected gene model can be found in NCBI at GenBank/BankIt using the accession BK014396 and archived in CaltechData here.
Special Characters of Gene Model
Improper alignment at start of coding exon three: As shown in Figure 1D, there is a stretch of amino acids (Figure 1D) that are not identical (black color), but similar (gray/white), between D. melanogaster and D. grimshawi. This pattern is also evident in a few other species as compared to D. melanogaster (Figure 1D). Though this is more obvious in D. kikkawai, D. serrata, D. obscura, D. pseudoobscura, D. persimilis, and D. miranda (Figure 1D) as compared to D. grimshawi (Figure 1D), it nonetheless exists.
Changes in the splice donor site for coding exon four: Rheb-PA in D. grimshawi has a canonical GT splice donor site at the end of coding exon four. In contrast, the end of coding exon four of Rheb-PA in D. melanogaster, and in most of the other Drosophila species across the genus Sophophora, use a non-canonical GC splice donor site.
Extended data:
Fasta (.faa and .fna) and GFF files are archived and available on CaltechData:
D_grimshawi_Rheb_geneModel_gff_faa_fna.
This file contains
- Peptide Sequence of Rheb in D. grimshawi
- Nucleotide Sequence of Rheb in D. grimshawi
- GFF of Rheb in D. grimshawi
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Katie M. Sandlin, Gary Williams, and Terence Murphy for their constructive criticism of this article.
References
Funding
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. IUSE-1915544 to LKR and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institute of Health Award R25GM130517 to LKR. The Genomics Education Partnership is fully financed by Federal moneys. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Reviewed By
Donald PriceHistory
Received: June 9, 2020Revision received: January 28, 2021
Accepted: January 31, 2021
Published: February 16, 2021
Copyright
© 2021 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Rele, CP; Williams, J; Reed, LK; Youngblom, JJ; Leung, W (2021). Drosophila grimshawi – Rheb. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000371.Download: RIS BibTeX