Present Address: Division of Biology and Biological Engineering and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA
Description
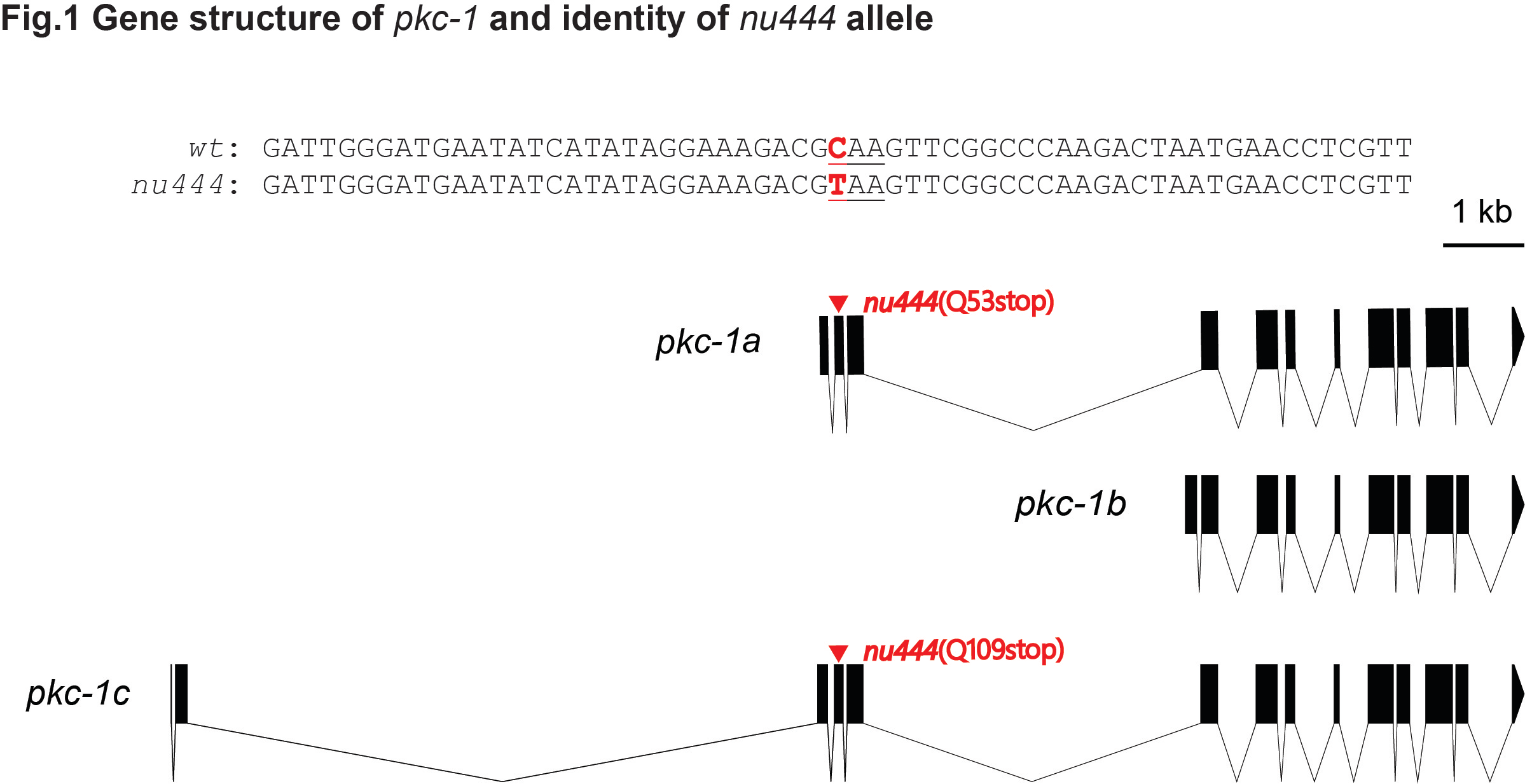
Here, we report nu444 as a novel allele of the gene pkc-1 that encodes the protein kinase C-1 in C. elegans. The nu444 allele was originally isolated from a forward genetic screen for mutants that suppressed the “Hic” (Hypersensitivity to Inhibitors of Cholinesterase) phenotype of dgk-1(nu62) mutants, which had increased acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction (Sieburth et al., 2007). In this screen, several genes that are important for neuropeptide secretion were recovered, including pkc-1(nu448) (Sieburth et al., 2007) and ric-7(nu447) (Hao et al., 2012). Sanger sequencing of the exons and exon-intron junctions of the pkc-1 locus revealed that nu444 had a nonsense mutation (C to T, in the coding strand of pkc-1, with left flanking sequence: 5’-GATGAATATCATATAGGAAAGACG-3’ and right flanking sequence: 5’- AAGTTCGGCCCAAGACTAATGAACC-3’) in an early exon that is only present in pkc1a and pkc-1c isoforms (Fig.1). Thus, pkc-1(nu444) allele is probably a null allele for both pkc-1a (Q53stop) and pkc-1c (Q109stop), but presumably does not affect pkc-1b.
References
Funding
Startup fund from University of Southern California, National Institute of Health R01 NS071085, and American Heart Association (to D.S.); fellowship from the NIH training program in Cellular, Biochemical, and Molecular Sciences at University of Southern California (to H.W.).
Reviewed By
Jordan WardHistory
Received: May 16, 2017Accepted: May 18, 2017
Published: May 18, 2017
Copyright
© 2017 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Wang, H; Sieburth, D (2017). nu444 is a novel allele of pkc-1 in C. elegans. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/W2Z59X.Download: RIS BibTeX