Description
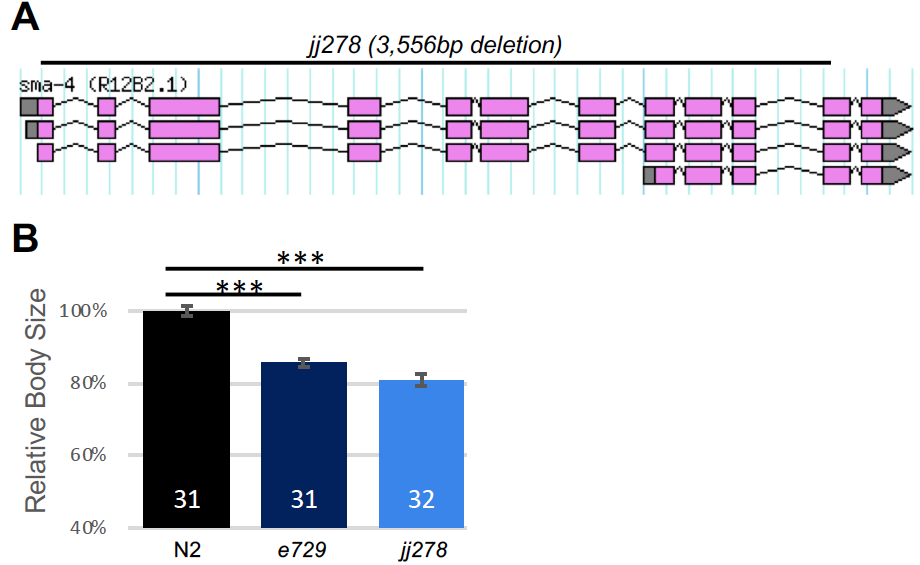
sma-4 encodes the co-Smad of the BMP pathway in C. elegans, which is also known as the Sma/Mab pathway (Savage et al. 1996). Null mutations in core components of this pathway, including the BMP ligand DBL-1, the receptors SMA-6 and DAF-4, and the R-Smads SMA-2 and SMA-3, all result in a small body size phenotype without significantly compromising viability (Gumienny and Savage-Dunn 2013). However, we found that even after multiple rounds of out-crossing, two deletion alleles of sma-4, ok3140 and tm4731, caused late larval lethality and embryonic lethality, respectively. This observation suggests that either SMA-4 has DBL-1/BMP-independent functions that are required for viability, or ok3140 and tm4731 have closely linked lethal mutations. To distinguish between these two possibilities, we generated a deletion allele of sma-4 using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated non-homologous end joining. This allele, jj278, contains a 3,556bp deletion (position: Chromosome III: 5,816,203….5,819,759) that deletes almost the entire coding region of sma-4 (Figure 1A) and represents a true molecular null. jj278 animals are viable and fertile, but are smaller than wild-type animals (Figure 1B), like loss-of-function mutants in other core BMP pathway members (Savage et al. 1996; Krishna et al. 1999). This result suggests that ok3140 and tm4731 likely have closely linked lethal mutations not caused by their respective sma-4 deletions.
Reagents
Plasmids and oligos used to generate jj278:
All sgRNA plasmids were using the pRB1017 backbone (ARRIBERE et al. 2014).
pJKL1171 (sma-4 N-sgRNA #1):
JKL-1692 (F): TCTTGGTCGAATAATGTTTCATCC
JKL-1693 (R): AAACGGATGAAACATTATTCGAC
pJKL1172(sma-4 N-sgRNA #2):
JKL-1694 (F): TCTTGACGGCTGAGATGTCATACC
JKL-1695 (R): AAACGGTATGACATCTCAGCCGT
pANM1 (sma-4 C-sgRNA #1):
ANM-12 (F): TCTTGCACTGTCAGGCATTATCGC
ANM-13 (R): AAACGCGATAATGCCTGACAGTGC
pANM2 (sma-4 C-sgRNA #2):
ANM-10 (F): TCTTGCAGCGATAATGCCTGACAG
ANM-11 (R): AAACCTGTCAGGCATTATCGCTGC
Oligos used to genotype jj278:
Expected sizes: Wild-type: 4.097kb + 295bp; jj278: 541bp
JKL-1104: CATGAATATGAGAAACTGCTGG
ANM-14: CCGTTGTCACCTCGAATCAC
ANM-15: GCTCTGCTCCATACAAAGGATC
Strain: LW5558: sma-4(jj278) III. Will be sent to the CGC.
References
Funding
National Institutes of Health R01 GM066953 and R01 GM103869 to J.L.
Reviewed By
Cathy Savage-DunnHistory
Received: October 29, 2018Accepted: November 8, 2018
Published: November 9, 2018
Copyright
© 2018 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
McKillop, AN; Shi, H; Liu, J (2018). A new deletion allele of sma-4. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/z4z9-ce10.Download: RIS BibTeX