Description
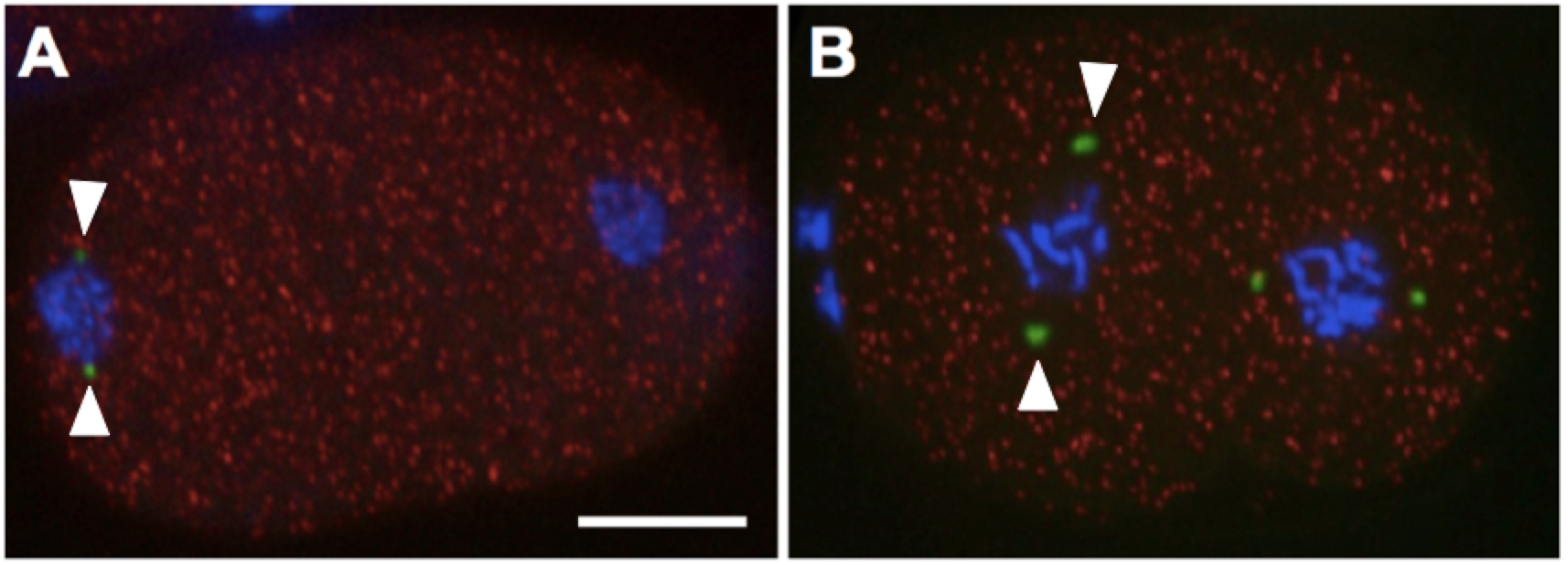
tbg-1 encodes gamma-tubulin, a ubiquitous and highly conserved component of centrosomes in eukaryotic cells (Strome et al, 2001). Using smFISH we determined the localization of tbg-1 transcripts (red). tbg-1transcripts are detected within distinct foci throughout the cytoplasm during both the first (A) and second (B) mitosis. tbg-1 transcripts are not enriched at centrosomes or either blastomere. In contrast, GFP tagged TBG-1proteins (green signal; arrowheads) localize at centrosomes, as previously shown (Strome et al, 2001). Shown are projections from selected focal planes. Bar=10μm.
New Findings: The first observation of tbg-1 mRNA localization in early C. elegans embryos.
Reagents
RNA probes targeting tbg-1 mRNAs (Quasar 670; red) were designed using Stellaris Probe Designer (Biosearch Technologies). smFISH was performed as described previously (Osborne-Nishimura et al., 2015; Shaffer et al., 2013). For hybridization, embryos were incubated with tbg-1 RNA probes (Quasar 670) at 39°C for four hours in the dark. Following hybridization, the embryos were washed and mounted with DAPI containing (blue) medium. To visualize centrosome-associated TBG-1 protein, we used transgenic strain that expresses GFP::TBG-1 (TH27; Hannak et al., (2002), green).
References
Funding
This work was done under a grant [7R15GM11016-02 to MHS] from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and research Excellence Fund from the Center of for Biomedical Research at Oakland University.
Reviewed By
Andy GoldenHistory
Received: August 18, 2017Accepted: August 23, 2017
Published: August 23, 2017
Copyright
© 2017 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
DeMeyer, L; Song, MH (2017). Localization of tbg-1 mRNAs and GFP::TBG-1 protein in Early C. elegans Embryos. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/W2CW8H.Download: RIS BibTeX