Description
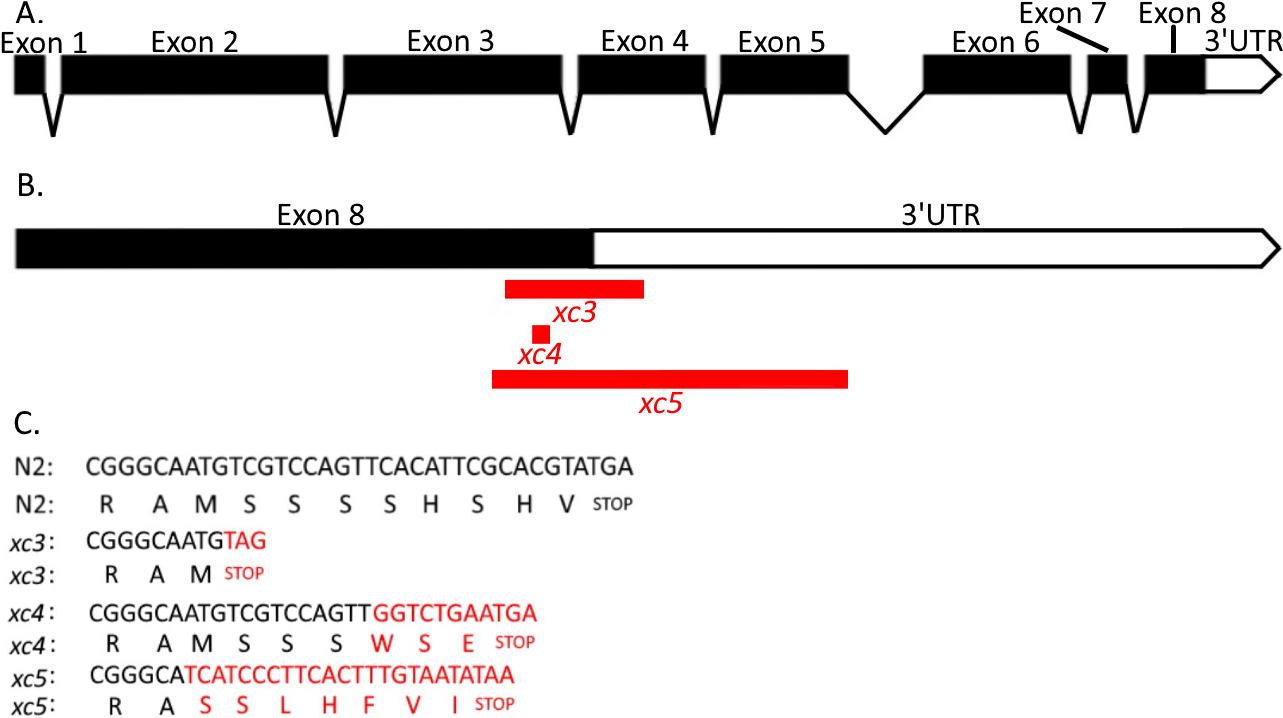
We have generated novel mutant alleles, named xc3, xc4, and xc5, of the gene cls-2 (R107.6) that encode one of the three predicted orthologs of mammalian CLASPs and of Drosophila ORBIT/MAST, microtuble-binding proteins (Akhmanova et al., 2001; Maiato et al., 2002). In C. elegans CLS-2 is required for meiosis and mitosis (Cheeseman et al., 2005; Dumont et al., 2010; Espiritu et al., 2012; Maton et al., 2015; Nahaboo et al., 2015). The alleles were isolated from gene mutations generated by Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ) mediated repair of Cas9-generated breaks (Dickinson et al., 2013; Ran et al., 2013). The alleles were detected by PCR using the following primers, 5’- CGATACGTCGGAGCAGAGC -3’ and 5’- CGGGGGTCGAAAATCATAAGG -3’. Next Generation Sequencing allowed us to identify 30 bp flanking sequences of the alleles xc3, xc4, and xc5 as TTGTCCAAGTCTACGTCAATCGGGCAATGT – [42 bp deletion] – AGCCCATAATTCCCCCGTATTCGTATCCCA, TCTACGTCAATCGGGCAATGTCGTCCAGTT – [3 bp deletion, 41 bp insertion (GGTCTGAATGACTTTCGCACTATTCCCCTATTCGCACGCCT)] – ATTCGCACGTATGATTCGTCGTTGCAATGT, and AACCTTGTCCAAGTCTACGTCAATCGGGCA – [111 bp deletion ] – TCATCCCTTCACTTTGTAATATAATTTTAT, respectively.
Based on information about cls-2 (R107.6) (WormBase, http://www.wormbase.org, WS261), the xc3, xc4, and xc5 mutant alleles effect the eighth exon and the 3’-UTR in the same way in each splicing isoform (Fig.1). In the xc3 mutant, 16 bp of the 3’UTR is deleted and a new stop codon was introduced after an 8 amino acid deletion (SSSSHSHV) of the C-terminus of the protein. In xc4 due to an insertion causing a frameshift mutation, 5 wildtype amino acids (SHSHV) from the C-terminus will be replaced by 3 amino acids (WSE). In xc5 the endogenous stop codon is deleted as well as 81 bp of the 3’UTR, while a new stop codon is introduced 21 bp after the mutation. Because of the deletion and new stop codon, in the xc5 mutant 9 amino acids (MSSSSHSHV) in the C-terminus of the protein will be replaced by 7 new amino acids (SSLHFVI). Previous researchers replaced serine residues with non-phosphorylatable alanine residues to study the effect of human CLASP2 phosphorylation (Kumar et al., 2017). The mutations we have generated have multiple serine residues deleted which presents a unique opportunity to study the effect of cls-2 (R107.6) phosphorylation. Since more of the 3’UTR is deleted in xc5 than xc3, the 3’UTR’s function could also be studied using these mutants.
Reagents
Alt-R® CRISPR-Cas9 crRNA
Alt-R® CRISPR-Cas9 tracrRNA
Alt-R® S.p. Cas9 Nuclease
Strains:
XC125 cls-2 (xc3) unc-119 (ed3) III; ieSi38 (IV)
XC126 cls-2 (xc4) unc-119 (ed3) III; ieSi38 (IV)
XC127 cls-2 (xc5) unc-119 (ed3) III; ieSi38 (IV)
References
Funding
NSF RUI 1244517, NIH R15 HD068996
Reviewed By
Andrea KalisHistory
Received: December 6, 2017Accepted: December 8, 2017
Published: December 19, 2017
Copyright
© 2017 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Munoz, NR; Black, CJ; Young, ET; Chu, DS (2017). New alleles of C. elegans gene cls-2 (R107.6), called xc3, xc4, and xc5. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/W2RQ2X.Download: RIS BibTeX