Present address: Winship Data and Technology Applications Shared Resource, Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University
Abstract
The notion of a two-hit or multi-hit model of carcinogenesis dates to at least the 1970’s and work done by Alfred Knudson. This concept was considered in the design and execution of a previous FLP/FRT screen in Drosophila melanogaster for conditional growth suppressors. During the course of this work, the lethal allele E7.25D.7 was identified as being of phenotypic interest. Here we report the genetic mapping of E7.25D.7, an allele of the sterile-20 kinase misshapen (msn).
Description
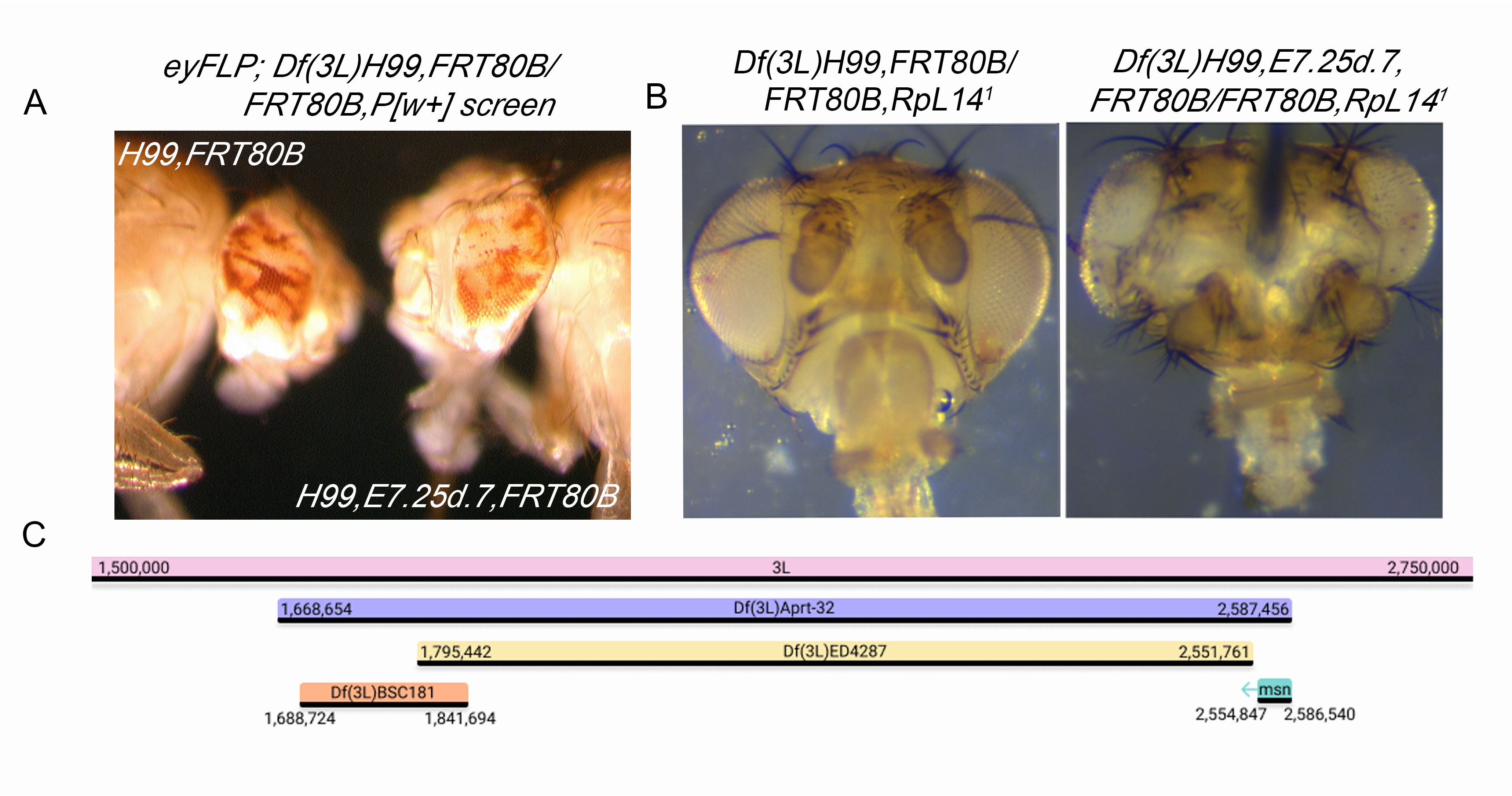
The lethal allele E7.25d.7 was isolated in a previously described FLP/FRT screen for conditional growth suppressors on chromosome 3L (Gilbert et al., 2011). Briefly, male w1118;; Df(3L)H99,FRT80B/TM6B flies were fed 25mM EMS and mated en mass to eyFLP;;ubi-GFP, FRT80B virgin females to screen a total of ~20,000 chromosome arms. Although most alleles from the screen were selected based on overgrowth of mutant white tissue relative to red wild-type twin spots, E7.25d.7 retained a mostly 50:50 white:red ratio, and apparent cell shape and bristle defects (Fig. 1A). To test whether our E725d.7 allele could synergize with Df(3L)H99 to override organ size controls, we crossed H99,E7.25d.7,FRT80B/TM6B to eyFLP;; RpL141,FRT80B/TM6B, a Minute allele (Saeboe-Larssen et al., 1997), thus allowing us to create entire heads that were mutant for E725d.7 and lacked developmental cell death. Compared to Df(3L)H99,FRT80B/FRT80B,RpL141 control heads, H99,E7.25d.7,FRT80B/FRT80B,RpL141 heads were larger and malformed, contained increased numbers of thick bristles, evidence of necrosis, and tumor-like morphological abnormalities (Fig. 1B). These phenotypes had different levels of expressivity, with females consistently exhibiting the most severe phenotypes.
In order to identify the gene, Df(3L)H99 was recombined off of the mutant chromosome, which was then checked for maintenance of lethality. E7.25d.7,FRT80B/TM6B female flies were then crossed in single vials to males from each of the 77 stocks of the Bloomington 3L Deficiency Kit (Cook et al., 2012). E7.25d.7 failed to complement Df(3L)Aprt-32 (3L: 1,668,654 … 2,587,456; Cook, 2016), but complemented Df(3L)BSC181 (3L: 1,688,724 … 1,841,694; BDSC, 2008) and Df(3L)ED4287(3L: 1,795,442 … 2,551,761; DrosDel Project, 2007) (Table 1). We obtained loss-of-function alleles for two candidates, daughter of sevenless (dosP115) and mishappen (msn102). msn102 failed to complement E7.25d.7. In a separate experiment E7.25d.7 failed to complement an independent allele of msn (msn172) (Table 2).
| Selected 3L deficiency stocks | |||
| Deficiency | BDSC Stock # | Genomic region | Complementation Test with E7.25d.7 |
| Df(3L)BSC181 | 9693 | 3L: 1,688,724 … 1,841,694 | Complement |
| Df(3L)Aprt-32 | 5411 | 3L: 1,668,654 … 2,587,456 | Non-Complement |
| Df(3L)ED4287 | 8096 | 3L: 1,795,442 … 2,551,761 | Complement |
| Single genes tested within the Df(3L)Aprt-32 deficiency region | |||
| Gene | BDSC Stock # | Allele | Complementation Test with E7.25D.7 |
| dos | 6845 | dosP115 | Complement |
| msn | 5945 | msn102 | Non-Complement |
| msn | 5947 | msn172 | Non-Complement |
msn encodes a ste-20-like Ser/Thr kinase of the MAPK4 family, and alleles were originally identified in two independent screens for genes required for eye development (Xu and Rubin, 1993), and those regulated by the photoreceptor transcription factor Glass (Treisman et al., 1997). The phenotypic abnormalities in the eye of the original msn alleles included cell shape and orientation changes in photoreceptors. It was also reported that msn transcripts are expressed in cells undergoing cell migration and shape changes, and ultimately it was hypothesized that Msn plays a role in cell signaling during cytoskeletal rearrangement. Msn has recently shown to act, along with other MAPK4-family kinases, to phosphorylate the Hippo pathway kinase Warts (Wts) to restrict Yorkie (Yki) activity (Meng et al., 2015; Li et al., 2015). Importantly, Msn activity is partially redundant to both Wts and other MAPK4 family members in restricting Yki activity, which could explain the conditional nature of the allele.
Reagents
Df(3L)H99,FRT80B/TM6B (Gilbert et al., 2011)
E7.25D.7,FRT80B/TM6B-GFP (this manuscript)
Df(3L)H99,E7.25D.7,FRT80B/TM6B, Tb (this manuscript)
yweyFLP;; P[m-w+]RpL141FRT80B, /TM6B (gift from K. Moberg)
eyFLP;;P[m-w+;ubiGFP]FRT80B (gift from K. Moberg)
Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center 3L Deficiency Kit
w*; P{lacW}dosP115 Diap11. Cu1 sr1/TM6B, Tb1(BDSC #6845)
w*;msn102P{neoFRT}80B/TM6B (BDSC #5945)
w*;msn172,P{neoFRT}80B/TM6B, Tb1 (BDSC #5947)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center and thank Chang-Soo Seong and K. Moberg for insightful comments and helpful discussion.
References
Funding
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant R01CA201340 to MGR
Reviewed By
AnonymousHistory
Received: April 15, 2021Revision received: July 13, 2021
Accepted: July 14, 2021
Published: July 22, 2021
Copyright
© 2021 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Kiely, E; Gilbert-Ross, M (2021). The conditional growth suppressor E7.25d.7 is an allele of the sterile-20 kinase misshapen. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000424.Download: RIS BibTeX