Abstract
We mapped rol-9 to the mlt-11 locus (encoded by the gene W01F3.3) on the far-right end of chromosome V. The canonical allele of rol-9, sc148, is an in-frame deletion in a conserved exon of the protein that creates a gain-of-function roller phenotype. sc148 deletes a short peptide of unknown function conserved in nematodes.
Description
rol-9 has long been used as a marker for the far-right end of chromosome V, but the identity of the protein encoded rol-9 is unknown. The canonical allele of the gene, sc148, is a strong semi-dominant right-hand roller (Bergmann et al., 1998). Another uncharacterized transposon insertion allele of rol-9, zu156 is also a strong roller (Susan Mango and Jim Priess, personal communications).
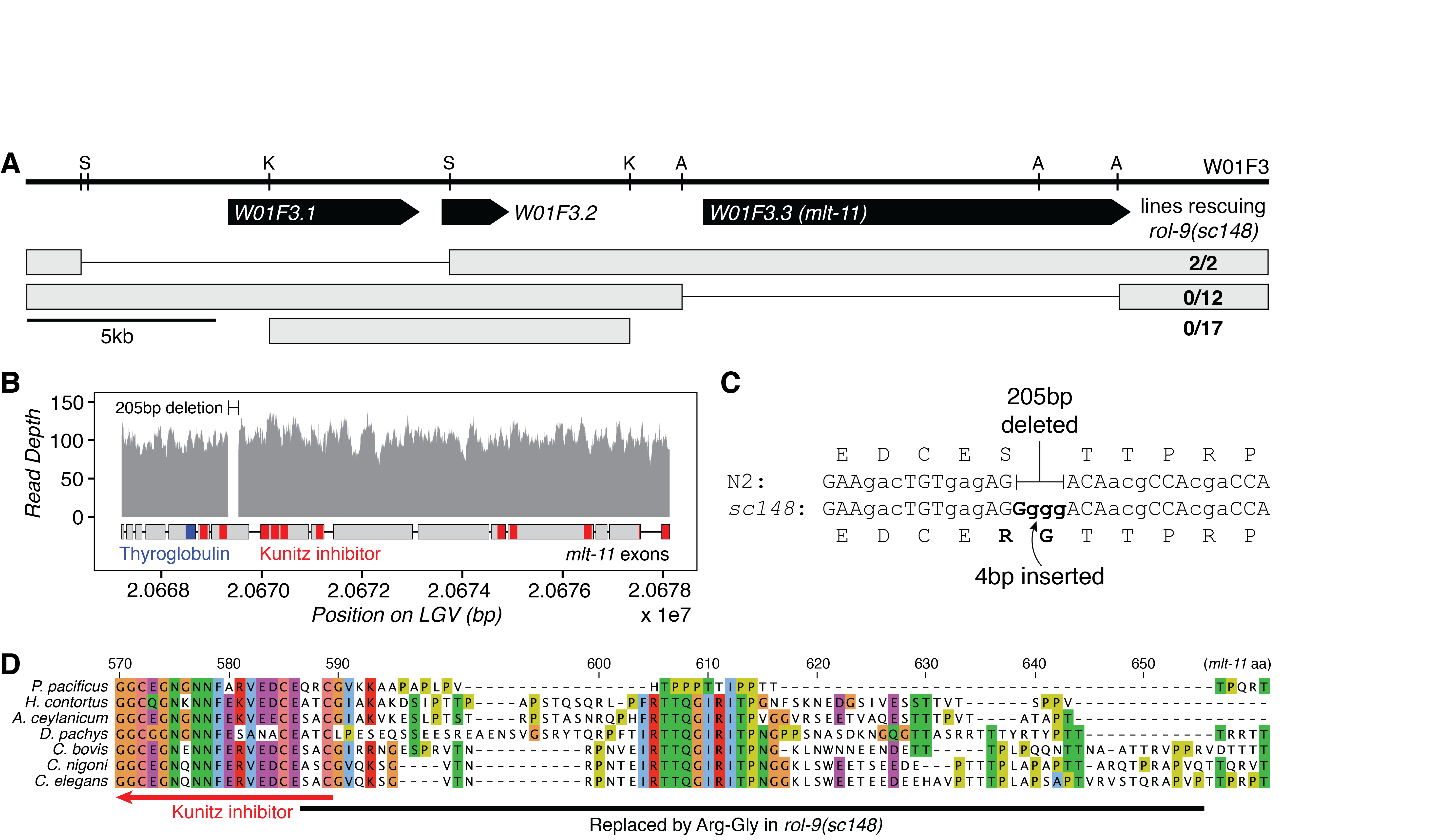
We mapped and cloned rol-9 while cloning pbo-5, the last gene on LGV (Beg et al., 2008). Injection of the fosmid W01F3 rescued rol-9(sc148) (EG1920). We then fragmented W01F3 by restriction digest and identified the gene encoding rol-9 to be W01F3.3 (Figure 1A). W01F3.3 encodes mlt-11, a 340kDa predicted serine endopeptidase inhibitor composed of one thyroglobulin repeat and ten Kunitz inhibitor domains (Frand et al., 2005). Knockdown of mlt-11 by RNAi induces semi-penetrant embryonic or L1 arrest (Gottschalk et al., 2005; Simmer et al., 2003; Sönnichsen et al., 2005) as well as defects during larval molting, for which the gene was named. Since rol-9(sc148) causes a semi-dominant roller, it is likely that the allele is a gain-of-function mutation, and not a null or hypomorphic allele of mlt-11.
We precisely mapped the mutation causing rol-9(sc148) using whole genome sequencing. There was only one mutation annotated to have high or moderate functional effect on the far-right arm of LGV: a 205 basepair deletion (V:20,669,331-20,669,536, Figure 1B) combined with a four-base insertion (GGGG, Figure 1C). The mutation is found in exon 7 of mlt-11, which is conserved in all splice isoforms, and replaces 68 residues with an arginine and glycine.
The deletion overlaps only 3 amino acids of a Kunitz-type inhibitor domain in the protein, and the deleted sequence matches no conserved domains in the NCBI Conserved Domain Database (Marchler-Bauer et al., 2015). A 13aa peptide in the deletion is highly conserved in the Rhabditina clade (Figure 1D). This peptide (IRTTQGIRITPNG) is almost perfectly conserved in Caenorhabditis, Haemonchus, and Ancylostoma, but is not conserved in Pristionchus. In all the species studied, this peptide is the only conserved sequence between the second and third Kunitz protease inhibitor domains. It is likely that the peptide was introduced into mlt-11 in the most recent common ancestor of Haemonchus and Caenorhabditis, after the split with Pristionchus.
Most genes with a roller phenotype encode structural constituents of the cuticle or collagens. It isn’t clear how sc148, a gain of function mutation in MLT-11, a molting protease inhibitor, induces a Rol phenotype, though it seems likely that the conserved peptide deleted in sc148 may be playing a Rol.
Methods
Request a detailed protocolFosmid rescue. rol-9(sc148) adult hermaphrodites were injected with either the full-length W01F3 fosmid or restriction fragments in which the fosmid was cut with either SacI, KpnI, or AatII. Fosmids were co-injected with a fluorescent marker to identify lines with extrachromosomal array transmission into the F2 generation. Transmitting lines were scored for rescue. EG1920 contains an extrachromosomal array containing the full-length W01F3 fosmid.
Whole genome sequencing and data analysis. rol-9(sc148) animals were grown on HB101 plates until near starvation, at which point genomic DNA was extracted using a Qiagen DNeasy Blood and Tissue kit. Genomic DNA libraries were prepared using a Nextera transposase kit (Illumina) and were sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq with 2×150 base reads. Library prep and sequencing were performed by the Huntsman Cancer Institute Genomics Core facility. Alignment and analysis of sequencing reads was performed by an in-house software pipeline. Briefly, reads were aligned to the C. elegans genome (WBcel276) using bwa (Li and Durbin, 2009) and processed with samtools (Li, 2011). Basecalling was performed using GATK4 (McKenna et al., 2010), and homozygous mutations with high genotype quality (GQ>20) were annotated with SNPeff (Cingolani et al., 2012). We identified the deletion in W01F3.3 algorithmically using smoove (Pedersen et al., 2020) and by eye using the Integrative Genome Viewer (Robinson et al., 2011).
Conservation analysis. Nematode orthologs of mlt-11 were identified using BLASTP (Altschul et al., 1990). Potential hits were defined as having an E-value less than 1e-100 and a protein length greater than 3000aa. The full-length sequences of these proteins were aligned using Clustal Omega (Goujon et al., 2010; Sievers et al., 2011). The sequences used in the alignment are: Caenorhabditis elegans (NP_001256938.1), Caenorhabditis nigoni (PCI30935.1), Caenorhabditis bovis (CAB3399020.1), Diploscapter pachys (PAV69501.1), Ancylostoma ceylanicum (EPB71358.1), Haemonchus contortus (CDJ84543.1), and Pristionchus pacificus (KAF8386888.1).
Reagents
The rol-9(sc148) allele in EG10047 was isolated as a segregant of a mapping cross (Beg et al., 2008). EG1920 contains an extrachromosomal array that rescues both rol-9(sc148) and pbo-5(ox9).
| Strain | Genotype | Source |
| EG10047 | rol-9(sc148) V | this study |
| EG1920 | rol-9(sc148) pbo-5(ox9) V; oxEx266[Psur-5::GFP, W01F3, purified yeast genomic DNA containing Δ200 (Y44A6 deletion from 5′ end of Y44A6A to 3′ end of W07A8)] | Beg et al. 2008 |
Acknowledgments
We thank Wayne Davis for comments on the manuscript and the Huntsman Cancer Institute Genomics core facility for performing genome sequencing. We thank the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) for providing strains.
References
Funding
This work was supported by funding the National Institutes of Health (NIH): R01GM095817 to EMJ. EMJ is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Reviewed By
AnonymousHistory
Received: November 24, 2021Revision received: December 15, 2021
Accepted: December 20, 2021
Published: January 5, 2022
Copyright
© 2022 by the authors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Citation
Rich, MS; Nix, P; Jorgensen, EM (2022). The C. elegans mapping locus rol-9 is encoded by a gain-of-function mutation in mlt-11. microPublication Biology. 10.17912/micropub.biology.000506.Download: RIS BibTeX